Human skin suppresses inflammation after exposure to ultraviolet

A study led by an NIHR Manchester Biomedical Research Centre scientist has identified, for the first time, how the human skin suppresses inflammation after exposure to ultraviolet radiation (UVR). Dr Nathan Hawkshaw is the lead author of a research paper published in Clinical & Translational Immunology, an open access, peer-reviewed journal.

Integrative Approaches to Sun Protection: Thinking Beyond Sunscreen
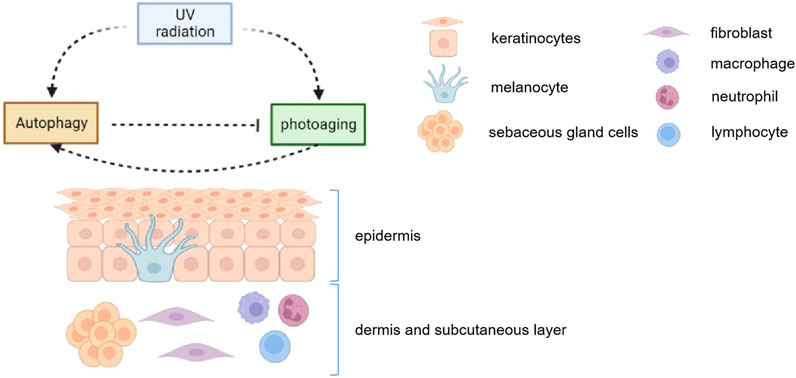
Frontiers Autophagy plays an essential role in ultraviolet radiation-driven skin photoaging
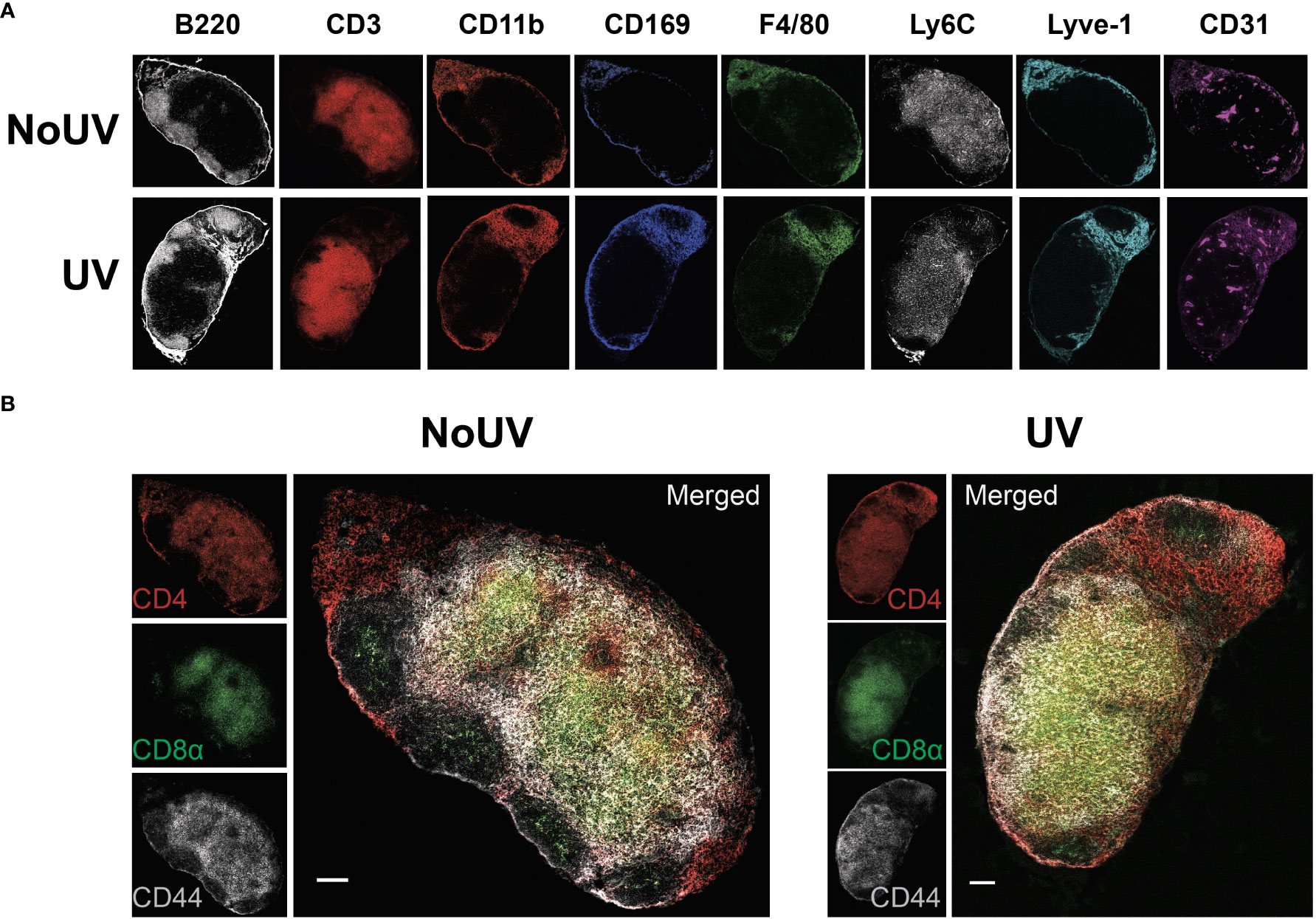
Frontiers Exposure to solar ultraviolet radiation establishes a novel immune suppressive lipidome in skin-draining lymph nodes
Quercetin suppresses MMP-1 and COX-2 expression and blocks collagen

Systemic immune by UV radiation. Exposing the skin to UV radiation

Human skin suppresses inflammation after exposure to ultraviolet radiation

Psoriasis - Life Extension

Ultraviolet Radiation From The Sun - Sunsafe Rx
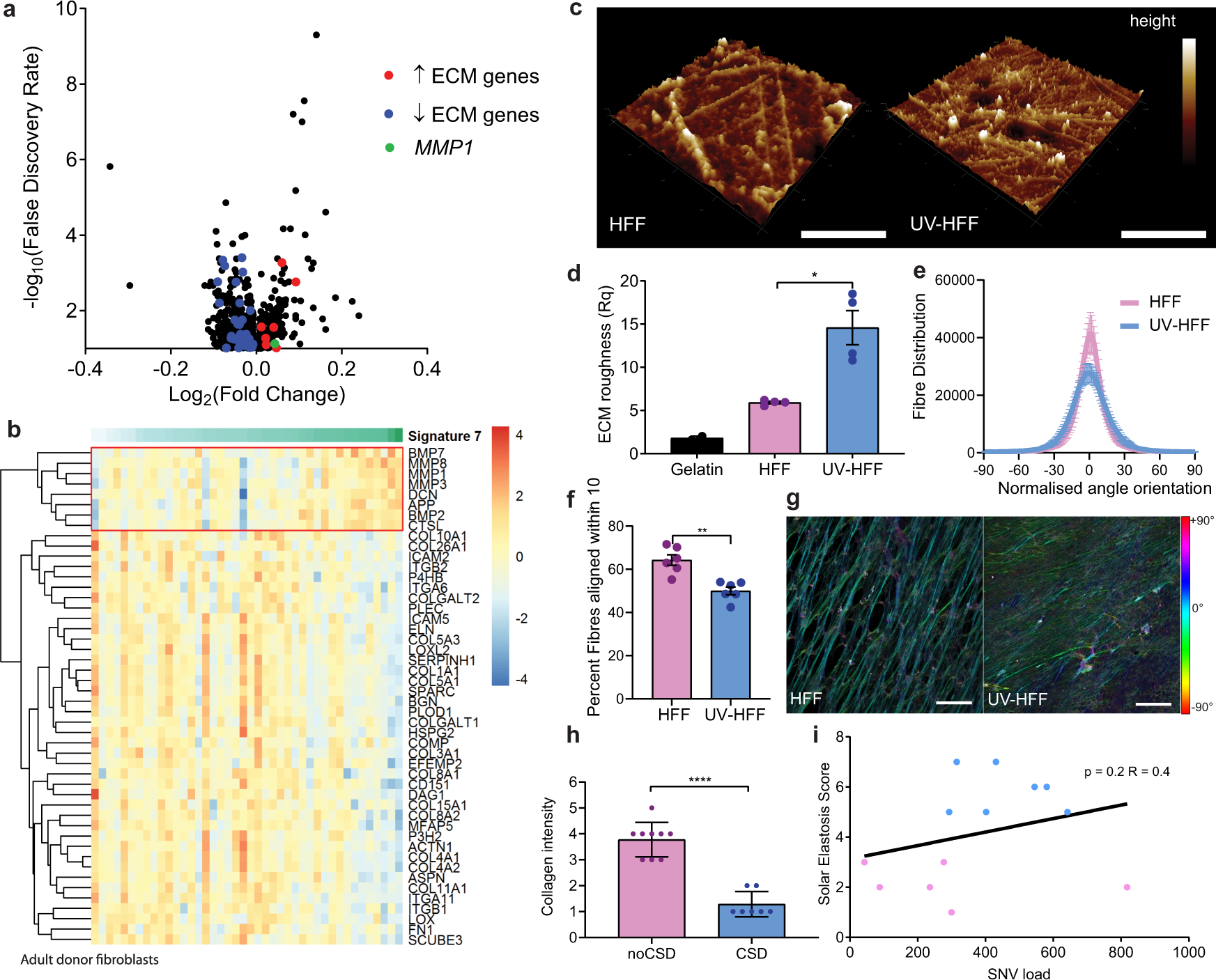
Ultraviolet light-induced collagen degradation inhibits melanoma invasion
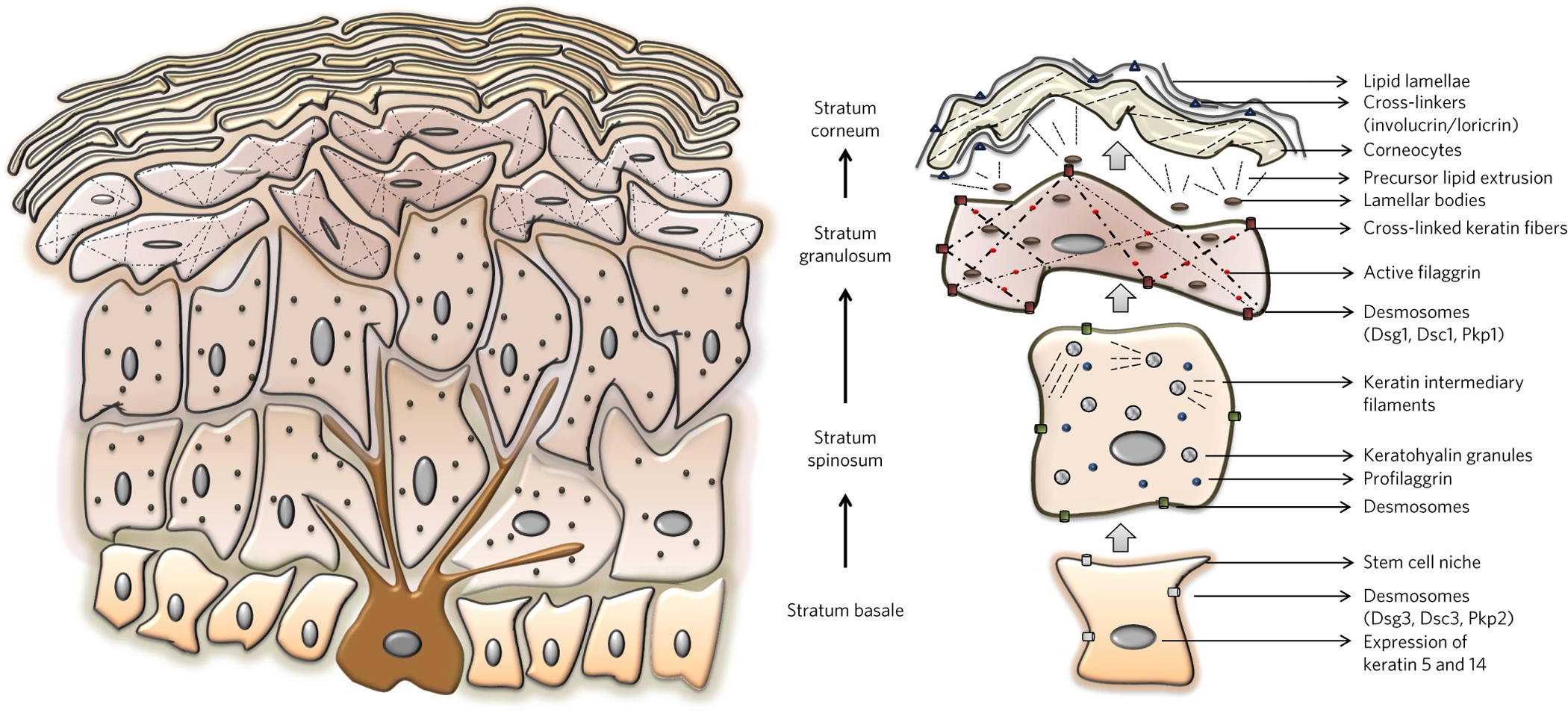
Multifaceted pathways protect human skin from UV radiation
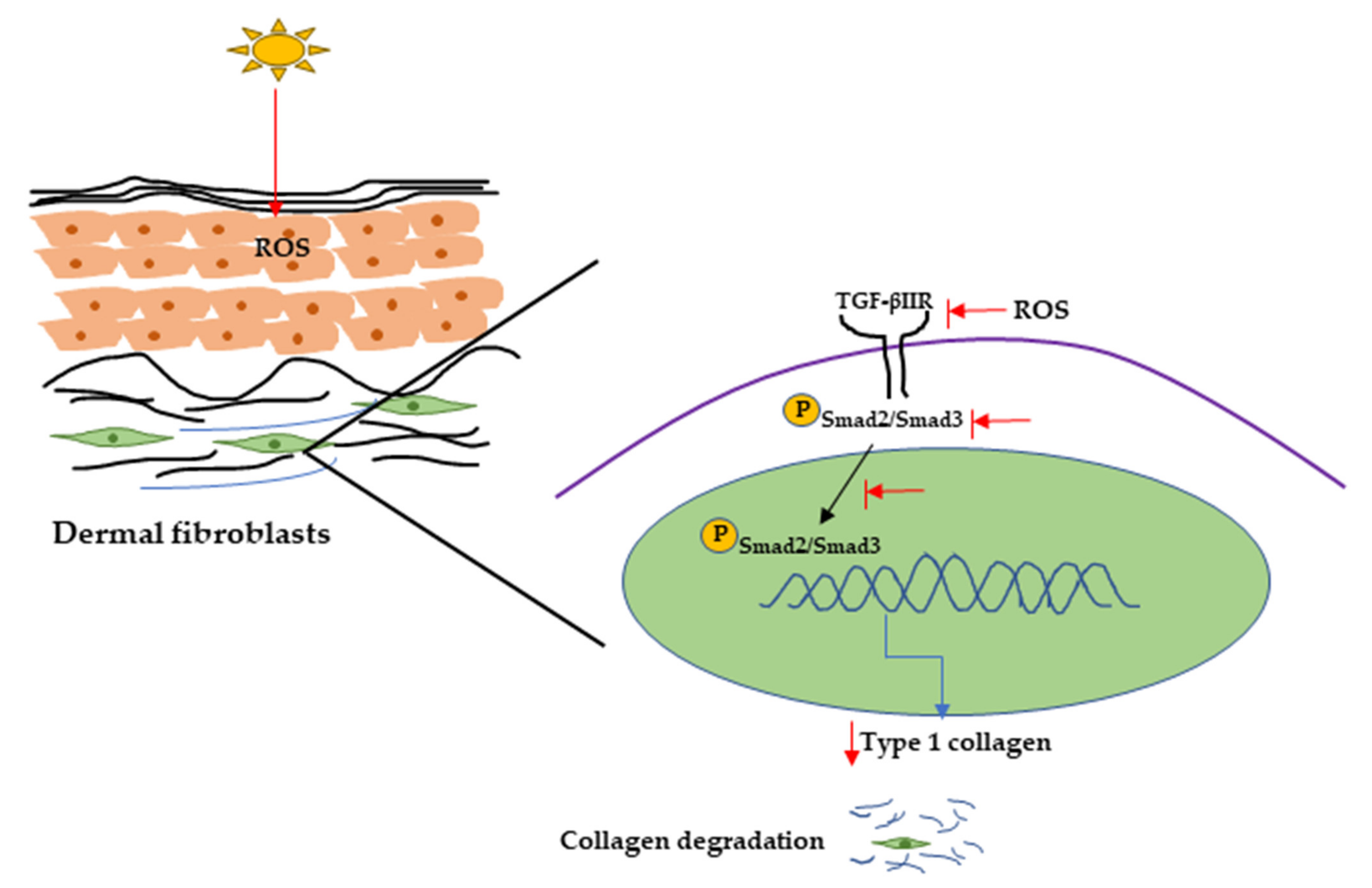
IJMS, Free Full-Text

Topical application of glycolic acid suppresses the UVB induced IL-6, IL-8, MCP-1 and COX-2 inflammation by modulating NF-κB signaling pathway in keratinocytes and mice skin - ScienceDirect
Sunburn: Background, Pathophysiology, Etiology

Quercetin inhibits UV irradiation-induced inflammatory cytokine production in primary human keratinocytes by suppressing NF-κB pathway.

4‐phenylpyridine suppresses UVB‐induced skin inflammation by targeting c‐Src in vitro and in vivo - Kim - 2022 - Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine - Wiley Online Library